
This is the latest update of 300-410 dumps in March 2023: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html, including 807 latest exam questions and answers, verified by a professional team, true and effective.
leads4pass 300-410 dumps comes with PDF and VCE learning methods, 300-410 dumps PDF is light and easy to read, and 300-410 dumps VCE is a friendly SaaS tool developed by the leads4pass IT team, simulating real scenarios to help candidates In practical practice tests, you can choose the habitual learning method at will.
Is the 300-410 ENARSI Certification Exam Difficult?
This is an enterprise advanced infrastructure certification exam. The exam content is relatively rich, and the random exam questions in the actual exam room vary greatly, so it is still relatively difficult, but don’t worry, candidates can help you pass the exam 100% through excess practice. leads4pass 300-410 dumps contain 807 300-410 ENARSI certification exam questions to meet the actual requirements.
Read a copy of the latest 300-410 dumps exam questions and answers online (Include Labs)

Share 300-410 exam questions and answers with labs (Questions 3)
| Type | Number of exam questions | Exam name | Exam code | Last updated |
| Free | 15 | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) | 300-410 | 300-410 dumps |
Question 1:
Refer to the exhibit.
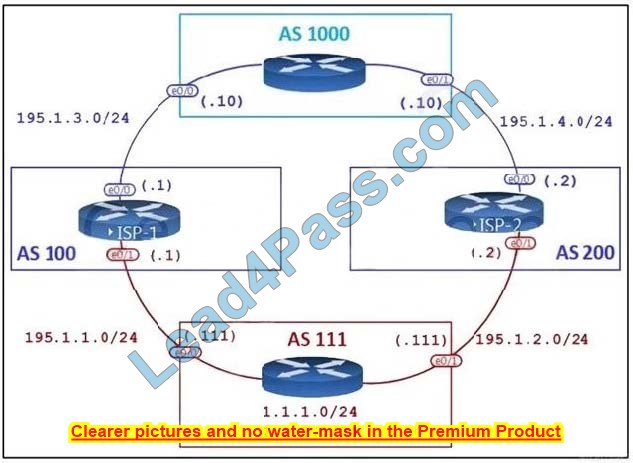

AS111 is receiving its own routes from AS200 causing a loop in the network. Which configuration provides loop prevention?
A. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.1.1 as-override no neighbor 195.1.2.2 allowas-in
B. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.2.2 as-override no neighbor 195.1.1.1 allowas-in
C. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.1.1 as-override neighbor 195.1.2.2 as-override
D. router bgp 111 no neighbor 195.1.1.1 allowas-in no neighbor 195.1.2.2 allowas-in
Correct Answer: D
Question 2:
You are using an aggregate static route to null 0 to redistribute static routes into BGP.
Which problem can result if the router loses access to one of these routes?
A. Black hole
B. Routing loop
C. Split horizon
D. Unstable BGP table
Correct Answer: A
If one of the aggregated routes is lost, the router will discard packets destined for that route. This condition is known as a black hole.
For example, suppose you have a number of subnets of range 11.1.0.0/16, all of which have 24-bit masks, such as 11.1.2.0/24. You aggregate them all to 11.1.0.0/16 and advertise that aggregate. If this router were to lose connectivity to one
of the subnets, for example, 11.1.3.0/24, then any traffic routed through this router to that subnet would never reach it, even if there were another valid path.
Split horizon is a loop avoidance mechanism that is by default always in effect, and is not affected by the loss of a subnet route that is part of an aggregate route.
BGP tables are not made unstable by the loss of a subnet route that is part of an aggregate route.
Routing loops would not occur simply from the loss of a subnet route that is part of an aggregate route.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify manual and auto summarization with any routing protocol
References:
Cisco > IP Routing: BGP Configuration Guide > BGP4 > Aggregating Route Prefixes Using BGP
Question 3:
Simulation Lab


Simulation Tasks A network is configured with CoPP to protect the CORE fouler route processor for stability and DDoS protection. As per company policy, a class named class-default is preconfigured and must not be modified or deleted. Troubleshoot CoPP to resolve the issues introduced during the maintenance window to ensure that:
1. Dynamic routing policies are under CoPP-CRITICAL and are allowed only from the 10.10.x.x range.
2. Telnet, SSH, and ping are under CoPP-IMPORTANT and are allowed strictly to/from 10.10.x.x to the CORE router (Hint: you can verify using Loopback1).
3. All devices ping (UDP) any CORE router interface successfully to/from the 10.10.x.x allow range and do not allow any other IP address. NORMAL (Hint: Traceroute port range 33434 33464).
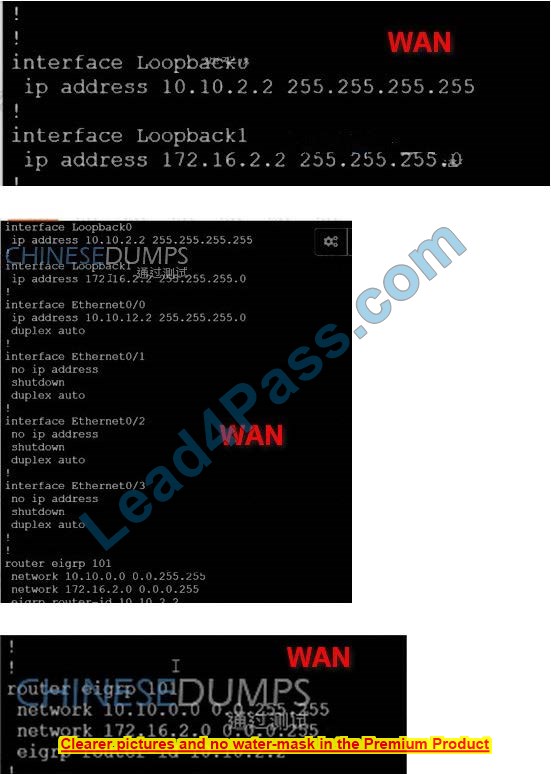

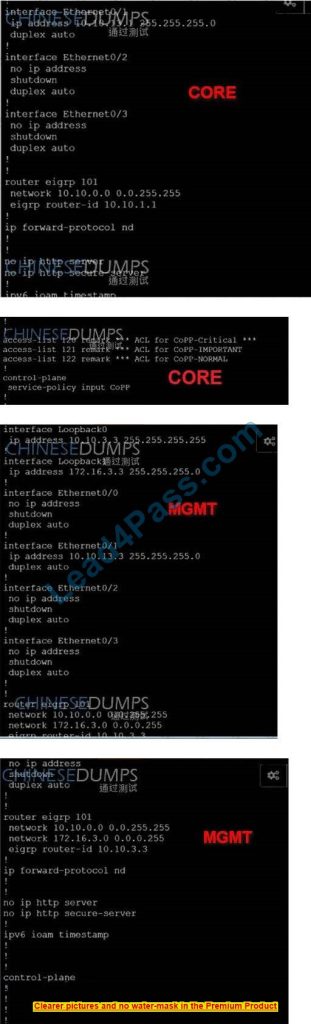
A. See the solution below in the Explanation.
B. PlaceHolder
C. PlaceHolder
D. PlaceHolder
Correct Answer: A
>>> CORE
policy-mao CoPP class CoPP-CRITICAL police 1000000 50000 50000 conform-action transmit exceed-action transmit
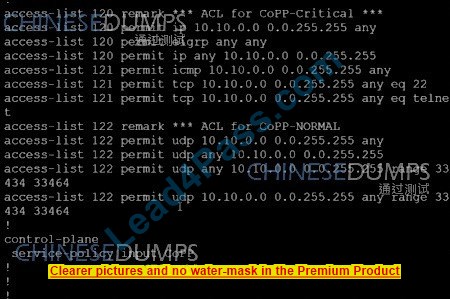
CORE# Copy run start >>> TESTING: CORE
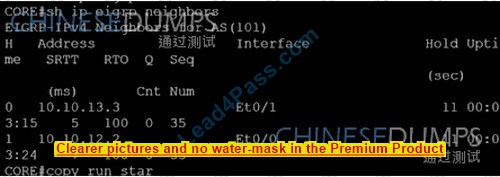
MGMT
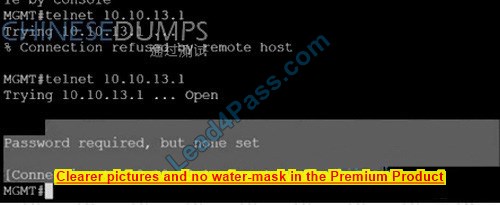
Question 4:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to connect to R1 via Telnet with no success.
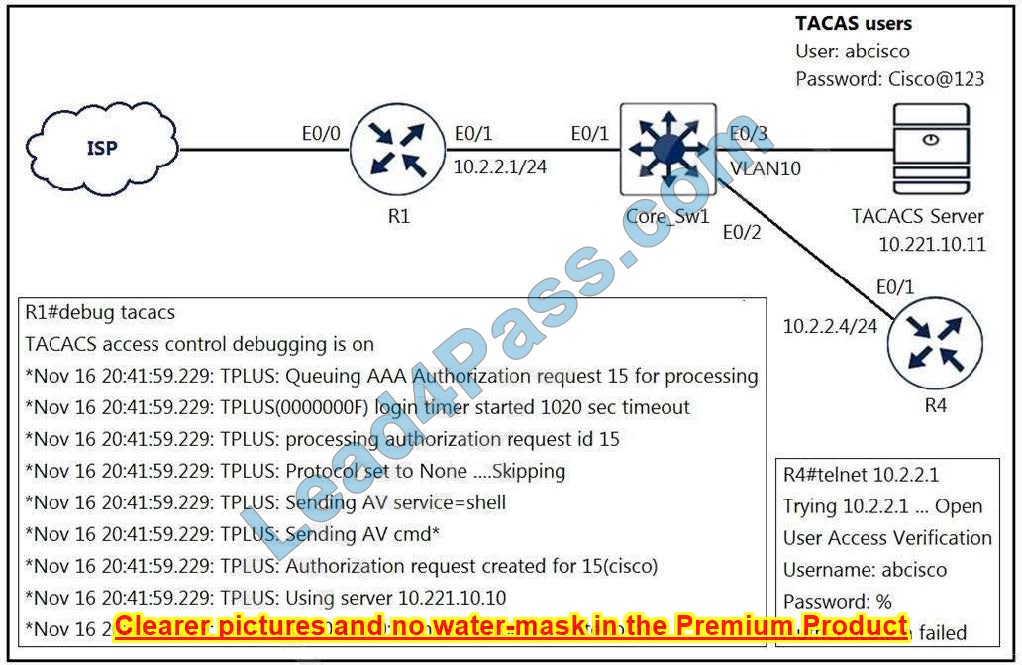
Which configuration resolves the issue?
A. tacacs server prod address ipv4 10.221.10.10 exit
B. ip route 10.221.10.10 255.255.255.255 ethernet 0/1
C. ip route 10.221.10.11 255.255.255.255 ethernet 0/1
D. tacacs server prod address ipv4 10.221.10.11 exit
Correct Answer: D
Looking at the debug output, second to the last line, the log suggests that it is attempting to use server x.x.10.10 when the diagram specifies that the server is actually x.x.10.11.
This would require the tacacs group to be modified to use the correct server:
`tacacs server prod`
`address ipv4 x.x.10.11`
`exit`
Question 5:
Which of the following commands need to be configured on a RIPng router prior to enabling this routing protocol?
A. ipv6 rip enable
B. ipv6 multicast-routing
C. ipv6 unicast-routing
D. ipv6 router rip
Correct Answer: C
The ipv6 unicast-routing command should be used before enabling RIPng on a router. This command should be executed in the global configuration mode of the router. IPv6 can then be enabled by using the ipv6 enable command on any of the interfaces of the router. The ipv6 unicast-routing command allows you to forward IPv6 unicast datagrams.
Routing Information Protocol Next Generation (RIPng) allows routers to learn about routes in an autonomous system. RIPng is an extension of the RIPv2 protocol to provide support IPv6 for future adherence.
The similarities between RIPv2 and RIPng are as follows:
Both protocols use User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Both use distance vector algorithms to find the best route.
Both of them measure the metric in terms of hops.
Both have the same maximum hop count of 15 for valid routes.
The differences between RIPv2 and RIPng are as follows:
RIPv2 learns IPv4 routes, whereas RIPng learns IPv6 routes
RIPv2 supports automatic summarization as IPv4 defines classful addresses, whereas RIPng does not support automatic summarization RIPv2 uses UDP port 520, whereas RIPng supports port 521
RIPv2 requires authentication for RIP packets, whereas RIPng does not require RIP-specific authentication as IPv6 has an in-built IPsec authentication
The ipv6 rip enable command should not be used because this command allows you to enable the IPv6 RIP routing process on the interfaces of a router.
You should not use the ipv6 multicast-routing command prior to enabling IPv6 on the router. This command is used after IPv6 is enabled on one or more interfaces of the router to allow multicast forwarding using Protocol Independent
Multicast (PIM) and Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) on all the IPv6-enabled interfaces.
The ipv6 router rip command should not be used prior to enabling IPv6 because it allows you to enter the RIP for IPv6 router mode.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe RIPng
References:
Cisco > Configuring IPv6 Routing
Cisco > Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference > ipv6 unicast-routing
Question 6:
A time-based access list has been configured on R1 to allow SSH access to the device only on weekdays. Which of the following are valid options when using the time range command? (Choose two.)
A. relative
B. recurring
C. absolute
D. periodic
Correct Answer: CD
Question 7:
Router R2 should be learning the route for 10.123.187.0/24 via EIGRP. Which action resolves the issue without introducing more issues?
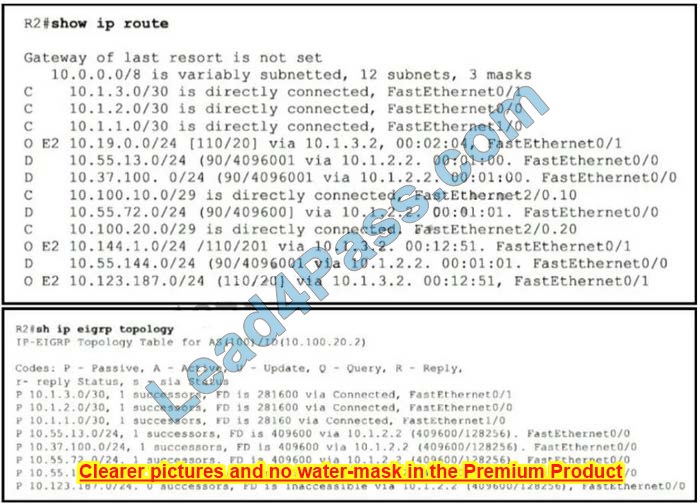
A. Remove route redistribution in R2 for this route in OSPF.
B. Use and distribute the list to modify the route as an internal EIGRP route.
C. Redistribute the route in EIGRP with metric, delay, and reliability.
D. Use distribute-list to filter the external router in OSPF
Correct Answer: D
Question 8:
Examine the exhibit.

You have determined that RTR2 is not advertising the CIDR summary address 192.168.0.0 to the other routers in AS 65100.
Which set of configuration commands will enable the BGP router RTR2 to announce the network prefix 192.168.0.0/16 to the other routers in the AS 65100?
A. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.3.0
B. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0
C. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 IP route 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null 0
D. router bgp 65100 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101 neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 IP route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0
Correct Answer: D
Issuing the following commands will cause RTR2 to advertise the CIDR block 192.168.0.0/16 to the other routers by using BGP:
RTR2(config)# router bgp 65100
RTR2(config-router)# neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101
RTR2(config-router)# neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
RTR2(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RTR2(config-router)# ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0 The network command specifies the address that will be inserted into the BGP table. Without the mask keyword, the classful network will be assumed. Because 255.255.0.0, or /16,
is not the natural mask for any Class C address, the mask keyword must also be specified. Thus, 192.168.0.0 and 255.255.0.0 identify the desired address and mask of the 192.168.0.0/16 network prefix.
The router checks the IP forwarding table for an exact match before it advertises the route. Without a matching entry in the IP forwarding table, that route will not be advertised. RTR2 must be able to advertise a CIDR block and not the
individual subnets. A static route is required because BGP requires that a match of the network prefix be present in the forwarding table when using the network command with the mask keyword. Therefore, to ensure an exact match for the
identified prefix exists in the IP forwarding table, and to ensure that the prefix will always be advertised, a static route for 192.168.0.0/16 to null 0 is also required.
The syntax for the network command is shown below:
network network-number [ mask network-mask ] [ route-map map-tag ]
The parameters are:
mask – This parameter is optional and identifies the network or subnetwork to advertise. route-map – This parameter is optional and identifies a preconfigured route-map that will be used to filter specific addresses from being advertised.
The following command set is missing the mask keyword in the network command and the command to create a static route to null 0. The address used in the network command is also incorrect. It should 192.168.0.0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.3.0
The following command set is missing the mask keyword in the network command and the command to create a static route to null 0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65101
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.0.0
The following command set uses an incorrect mask (255.0.0.0) in the command that creates the static route to null 0. It should be 255.255.0.0:
router bgp 65100
neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65100
neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65100
network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
ip route 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 null 0
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe, configure, and verify BGP peer relationships and authentication
References:
Internetworking Case Studies > Using the Border Gateway Protocol for Interdomain Routing > Controlling the Flow of BGP Updates > CIDR and Aggregate Addresses > Aggregation and Static Routes
Question 9:
Refer to the exhibit. R2 is a route reflector, and R1 and R3 are route reflector clients. The route reflector learns the route to 172.16.25.0/24 from R1, but it does not advertise to R3. What is the reason the route is not advertised?
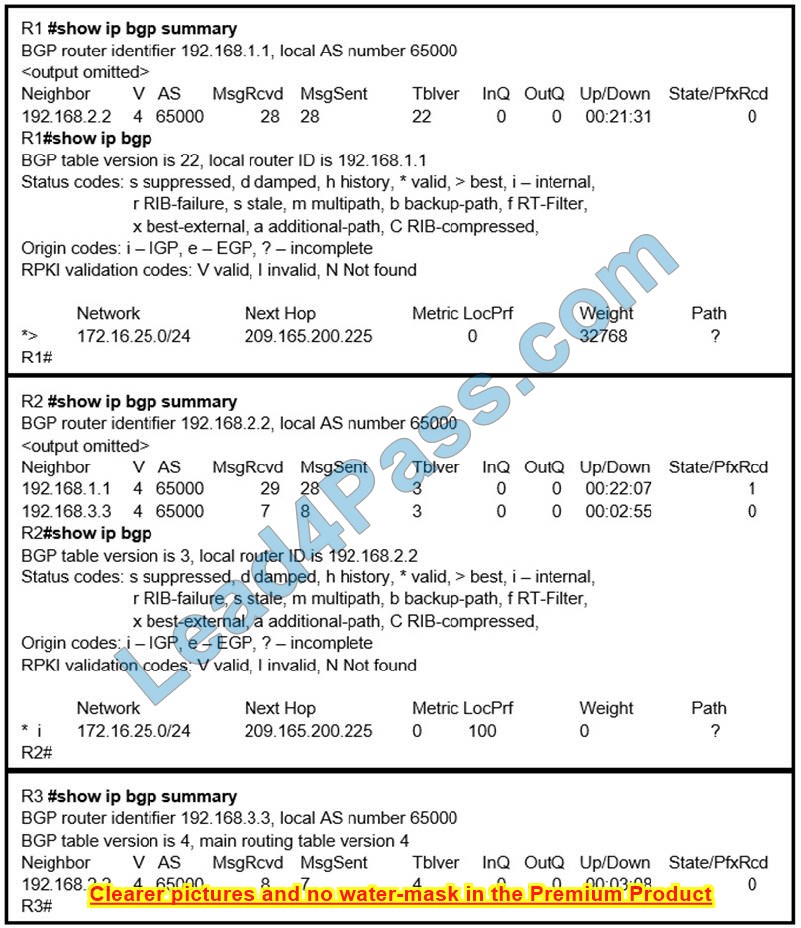
A. R2 does not have a route to the next hop, so R2 does not advertise the prefix to other clients.
B. Route reflector setup requires full IBGP mesh between the routers.
C. In route reflector setup, only classful prefixes are advertised to other clients.
D. In route reflector setups, prefixes are not advertised from one client to another.
Correct Answer: A
Question 10:
Refer to the exhibit. Mutual redistribution is enabled between RIP and EIGRP on R2 and R5. Which configuration resolves the routing loop for the 192.168.1.0/24 network?
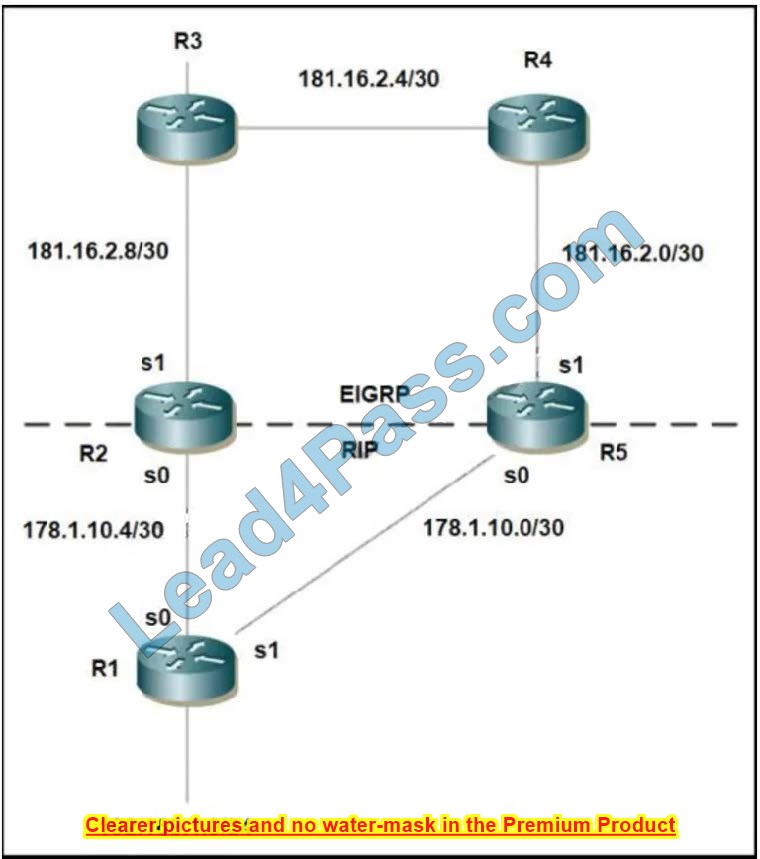
A. R2: router eigrp 10 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s1! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any R5: router eigrp 10 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s0! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any
B. R2: router eigrp 10 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s0! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any R5: router eigrp 10 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s0! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any
C. R2: router eigrp 10 network 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s0! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any
R5: router eigrp 10 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s1! router rip network 178.1.0.0 redistribute eigrp 10 metric 2 ! access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0 access-list 1 permit any
D. R2: router eigrp 7 networks 181.16.0.0 redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1 distribute-list 1 in s1!
router rip
network 178.1.0.0
redistribute eigrp 7 metric 2
!
access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0
access-list 1 permit any
R5:
router eigrp 7
network 181.16.0.0
redistribute rip metric 1 1 1 1 1
distribute-list 1 in s1
!
router rip
network 178.1.0.0
redistribute eigrp 7 metric 2
!
access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.0
access-list 1 permit any
Correct Answer: D
Question 11:
Refer to the exhibit. A junior engineer configured SNMP to network devices. Malicious users have uploaded different configurations to the network devices using SNMP and TFTP servers.
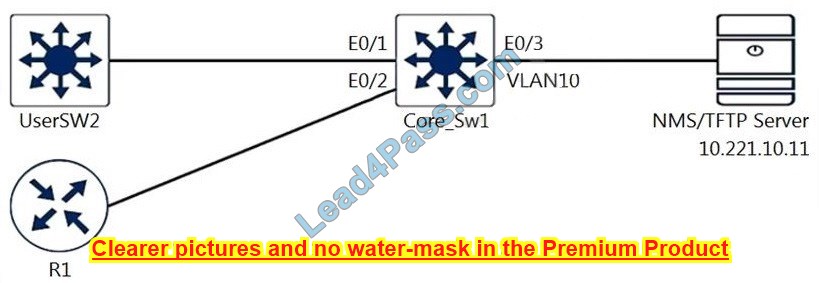
snmp-server group NETVIEW v3 priv read NETVIEW snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN snmp-server community Cisc0Us3r RO snmp-server community Cisc0wrus3r RW
Which configuration prevents changes from unauthorized NMS and TFTP servers?
A. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 deny any log! snmp-server group NETVIEW v3 priv read NETVIEW access 20 snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN access 20 snmp-server community Cisc0Us3r RO 20 snmp-server community Cisc0wrus3r RW 20 snmp-server tftp-server-list 20
B. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 deny any log! snmp-server group NETVIEW v3 priv read NETVIEW access 20 snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN access 20 snmp-server community Cisc0wrus3r RO 20 snmp-server community Cisc0Us3r RW 20 snmp-server tftp-server-list 20
C. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11 access-list 20 deny any log
D. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11
Correct Answer: A
Question 12:
What is the function of BFD?
A. It provides uniform failure detection regardless of the media type.
B. It creates high CPU utilization on hardware deployments.
C. It negotiates to the highest version of the neighbor version differs.
D. It provides uniform failure detection on the same media type.
Correct Answer: A
Question 13:
SNMPv2 has been used throughout a network to manage all of the network devices. You have been asked to migrate to an SNMPv3 solution instead. What is the biggest advantage of migrating from SNMPv2 to SNMPv3?
A. Enhanced security, including encryption of passwords
B. Enhanced performance, supporting more messages per minute.
C. Enhanced scaling, supporting thousands more devices per network segment than SNMPv2.
D. Using a push model instead of a pull. SNMPv3 uses telemetry to push data to SNMP management stations in real-time.
Correct Answer: A
Question 14:
You have implemented IPv6 automatic 6-to-4 tunneling between three IPv6 subnets as shown in the network exhibit. (Click the Exhibit(s) button.)

You have used the following commands to implement the automatic 6-to-4 tunnel:
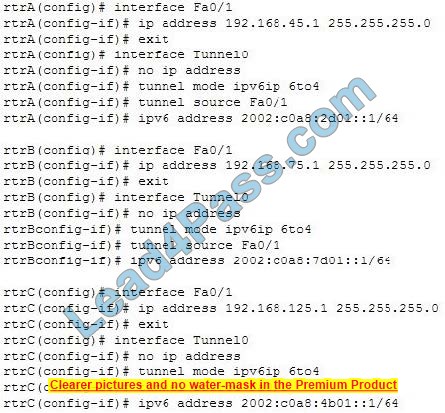
Your supervisor has assigned the task of verifying the automatic 6-to-4 tunnel to one of your colleagues. Your colleague runs the show running-config command and finds that incorrect IPv6 addresses have been assigned to the tunnel interfaces of the routers.
Which of the following IPv6 addresses should be assigned to rectify the problem? (Choose two.)
A. 2002::c0a8:2d01/64 to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrA
B. 2002:c0a8:4b01::1/64 to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrB
C. 2002:c0a8:7d01::1/64 to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrC
D. 2002:c0a8:4b01::1/64 to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrA
Correct Answer: BC
The 2002:c0a8:4b01::1/64 and the 2002:c0a8:7d01::1/64 IPv6 addresses should be assigned to the Fa0/1 interfaces of rtrB and rtrC, respectively. Automatic 6-to-4 tunnels embed the IPv4 address of the tunnel interfaces into the second and third quartets of the IPv6 address that has the 2002::/16 prefix.
To assign IPv6 addresses to the tunnel interfaces, perform the following steps:
1.
Convert the IPv4 address of the tunnel interface into binary.
2.
Convert the binary equivalent of the IPv4 address into hexadecimal (IPv6).
3.
Append the hexadecimal equivalent to the 2002::/16 prefix to form the IPv6 prefix of the tunnel interface.
For the Fa0/1 interface of rtrB, its IPv4 address of 192.68.75.1 is equivalent to the IPv6 address c0a8:4b01. This address is then appended to the 2002::/16 prefix, resulting in 2002:c0a8:4b01::/48. The remaining host bits can be filled with
zeros. Similarly, the IPv4 address of the Fa0/1 interface of rtrC is converted to the IPv6 address 2002:c0a8:7d01::/48.
The 2002::c0a8:2d01/64 IPv6 address should not be assigned to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrA. The Fa0/1 interface of rtrA has the IPv4 address 192.168.45.1. The IPv6 equivalent of the IPv4 address, which is c0a8:2d01, should be embedded in
the second and third quartets of the IPv6 address instead of the seventh and eighth quartets. IPv4 addresses are embedded into the last 32 bits for ISATAP tunnels.
The 2002:c0a8:4b01::1/64 IPv6 addresses should not be assigned to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrA. This IPv6 address is the equivalent of the IPv4 address 192.168.75.1, which is the address of the Fa0/2 interface of rtrB and not rtrA. Therefore,
this IPv6 address should be assigned to the Fa0/1 interface of rtrB.
Objective:
Network Principles
Sub-Objective:
Recognize proposed changes to the network
References:
Cisco Press > Articles > Cisco Certification > CCNP > CCNP Self-Study: Advanced IP Addressing Cisco Press > Articles > Network Technology > General Networking > Cisco Self-Study: Implementing Cisco IPv6 Networks (IPV6) Cisco >
Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Version 6 (IPV6) > Configure > Configuration Examples and Technotes > IPv6 Tunnel Through an IPv4 Network Cisco IOS IPv6 Implementation Guide, Release 15.2MandT > Implementing Tunneling for
IPv6
Question 15:
Users were moved from the local DHCP server to the remote corporate DHCP server. After the move, none of the users were able to use the network. Which two issues will prevent this setup from working properly? (Choose two)
A. Auto-QoS is blocking DHCP traffic.
B. The DHCP server IP address configuration is missing locally
C. 802.1X is blocking DHCP traffic
D. The broadcast domain is too large for proper DHCP propagation
E. The route to the new DHCP server is missing
Correct Answer: BE
…
Download 807 300-410 actual exam questions and answers: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (300-410 dumps), the best material for the actual 300-410 ENARSI certification exam.
Summarize:
All Cisco certification exams are relatively difficult, and it is not easy to obtain a certification. Candidates can only hope to pass the exam once they are fully prepared.
Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification exam is to test knowledge of implementation and troubleshooting of advanced routing technologies and services, by studying and using leads4pass 300-410 dumps practice test can help Them boost to 100% sure.